VR Prawn Dissection: Bringing Realism to University Biology Courses
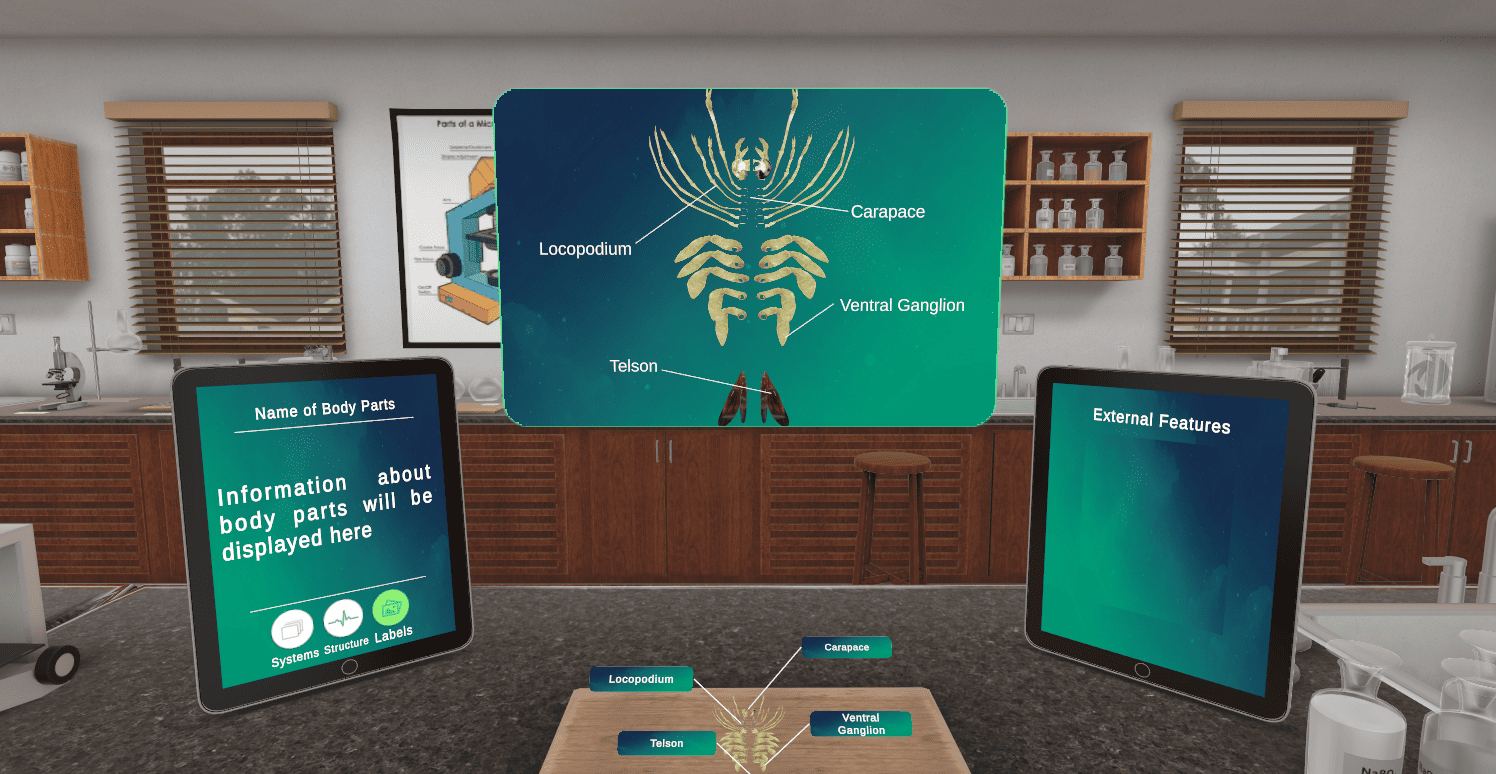
Picture Sarah and Alex, two biology majors attending a university. They put on VR headsets, which instantly transport them to a virtual lab where they can look at prawn anatomy in 3D.
By rotating the specimen, zooming in on minute structures, and even dissecting virtually with no concern for messing up, they can try it all out. It’s simply not possible to achieve this level of engagement in a traditional lab setting.
As educators, you face the challenge of keeping the educational integrity and engaging students. In this blog, we discuss how VR prawn dissection can serve as a bridge between traditional and modern educational needs.
Let’s get started.
What Needs to Be Changed?

Traditional dissection has been a mainstay of biology education for decades. However, it comes with several challenges:
Logistical Issues: Running dissection labs is time-consuming and resource-intensive, which is not the case with simulated labs.
Ethical Concerns: Personal or cultural beliefs make many students uncomfortable with using real specimens.
Cost Implications: As educational budgets tighten, cadaver supplies are becoming increasingly expensive to maintain.
So what is the solution then? Which technology do educators have their eyes set on? Let’s recount a short story first, that took place in a small classroom in Taiwan.
The Backstory: When did Educators Realise the Need for Transformative VR solutions?
Dr. Tzung Fang Chuang experienced firsthand the power of Virtual Reality (VR) in biology education when he introduced immersive VR dissection technology in college classrooms.
The students — especially those who had a hard time in traditional learning like Mia — put on headsets and moved around to explore 3D models of human organs
They felt excited about and understood the lesson. Dr. Chuang's research findings that included students using VR showed significantly improved comprehension of complex biological concepts compared to their counterparts using traditional textbook instruction, with pre – and post–assessments showing a statistically significant increase in assessment scores.
Moreover, 95% of students reported being more involved and interested in taking up future classes in biology from the experience of virtual reality.
In addition, Dr. Chuang's research demonstrated VR for medical education not only increases knowledge acquisition but also promotes collaboration among students, as students discuss their discoveries in VR.
The study included 138 high school students across several classrooms and showed that immersive VR could fill the gap between traditional learning methods and today's educational needs.
After finding that 70 percent of respondents stated they developed critical thinking skills with VR and 90 percent of them enjoyed using VR more than traditional methods, Dr. Chuang realised VR could bring a new era of biology education and inspire a future generation of learners.
Educational VR Simulation Biology: The Rise
A virtual reality dissections module transforms science education or biology courses in the changing world of education. In the case of that classroom, students can dissect prawns using virtual reality, not scalpels.
This approach represents an innovative method for realising realism and understanding complex biological systems.
At the University of Toronto, they integrated VR into their environmental science curriculum allowing students to learn interactively about aquatic ecosystems.
Again, Interactive prawn anatomy VR modules were adopted at Georgia Tech University, allowing students to dissect multiple specimens at the same time, without resource constraints.
Let’s look at the following research findings-
• A study conducted by PwC revealed that VR-based training can improve learner engagement by 400%.
• The University of Maryland conducted a study that found students who used VR tools, scored 30% higher on assessments than students in traditional settings.
This statistic shows just how effective immersive VR is for biology students to better understand complex anatomical relationships.
• Using VR in education makes the learners four times more focused in the curriculum, and leads to 30% more retention of learning outcomes.
VR dissection is also inclusive. The virtual environment allows students who may have felt uncomfortable or had ethical concerns in the past to be fully engaged in hands-on dissections.
An example of this is that engineering colleges such as Stanford have successfully infused VR into their curricula so that all students can make meaningful use of it.
 Get the App from Meta Store: Download Now
Get the App from Meta Store: Download Now
What If Learners Are Not Introduced To VR-based Prawn Dissection?
First, let us see what constraints enthusiastic learners like Alex and Sarah would have to face in Biology education in the absence of cutting-edge VR technologies-
Decreased Student Engagement and Interest
Alex and Srah who are experiencing an interactive digital world of learning may not be caught by traditional methods of dissection.
Inadequate use of innovative methods of teaching can decrease students' motivation and interest in biology courses, which might yield a decrease in enrollment in these programs.
In JISC’s survey report from 2029, students, teachers, and educators from all over the globe took part. The survey revealed that 82% of the attendees were very keen on trying out VR/AR technologies in education.
This signals a shift towards education 4.0, which involves the use of interactive elements in education, as facilitated by technologies like AR and VR.
Inequity in Learning Opportunities
Trying to continue traditional dissection allows for the number of students who have ethical concerns, or are uncomfortable with handling live specimens, to be greatly limited.
The inequity this causes further limits their ability to 'participate fully in the process of learning, understanding and achieving'.
Limited Skill Development for Future Professionals
With an ever-growing emphasis on technology bringing about the transformation of medical education, students who are only trained with traditional dissection may be unprepared for the modern healthcare world.
If they cannot use advanced tools like virtual reality it might keep them from being able to develop their skills and may reduce their competitiveness in the job market.
Conclusion
With the ever-increasing digital world, the use of virtual reality labs for higher education is a large step up for the biology education field.
This technology is an opportunity, offering educators ways to create engaging, real experiences for students — but at the same time address concerns around ethical issues that may accompany some traditional methods.